Warm summer in the forecast as droughts and wildfire risks loom: Weather Network
By Canadian Press on May 28, 2025.
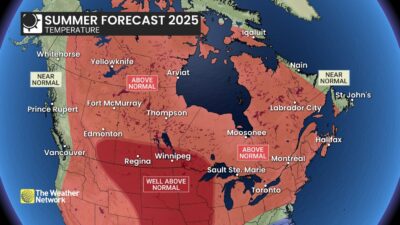
Canadians longing for sunshine and warmth will likely be pleased by a summer forecast that has an abundance of both, says Weather Network meteorologist Doug Gillham, but he cautioned the season “will highlight that you can get too much of a good thing.”
Droughts, wildfires and powerful thunderstorms could be in the works across parts of Canada this summer, with warmer-than-normal temperatures possible for the vast majority of the country, according to The Weather Network’s seasonal forecast for the months of June, July and August.
“I think most people are going to be happy when they see the forecast initially,” said Gillham, manager of The Weather Network’s forecast centre, ahead of the release of Wednesday’s forecast.
“But some disclaimers as well in that this summer can have some difficulties that come with extreme heat and not enough rain in parts of the country and stormy weather in other parts of the country.”
A warm and humid summer is forecasted for much of Ontario and Quebec and into the Maritimes, Gillham said.
Muggy conditions are expected to fuel some powerful thunderstorms and keep overnight temperatures warm across much of Central Canada, he said. Some heat waves are to be expected, possibly before July, but forecasters do not expect persistent heat in the region, except for areas west of Lake Superior.
Conditions get warmer and drier than normal as the forecast moves to the Ontario-Manitoba boundary, where wildfires have already offered a preview of the risks at play this summer. Several communities have evacuated in recent days as fast-moving fires tear across the region.
“We need to be extra vigilant this summer and really hope that we don’t get those fires started because conditions will be more conducive to fire spreading if they do start,” Gillham said.
What meteorologists consider normal has also changed as the planet warms up, largely due to heat-trapping fossil fuel emissions.
The forecasts of above- or below-normal temperatures and precipitation are based on average conditions over the past roughly 30 years. Yet, average Canadian summer temperatures have warmed by almost two degrees since the late 1940s, weather station records indicate, contributing to more intense wildfires, droughts and heat waves.
“It shifts the goalposts and the range of possibility,” Gillham said.
“It makes a cooler summer less likely. It makes a warmer summer more likely, but it’s not a linear progression.”
Drought could be a serious concern across the southern part of the Prairies where well above-normal temperatures are expected to combine with below-normal levels of precipitation, Gillham said. The upshot is that conditions are better leading into the summer than they have been in some recent tough drought years, such as 2012, he said.
The forecast still calls for warmer-than-normal temperatures for northern parts of Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, but with near-normal precipitation.
The “big picture” forecast has some similarities to the summer of 2021, Gillham said – a season marked in Western Canada by drought, wildfires, water shortages and a deadly heat wave over British Columbia.
“When you look at big picture (it) has some similarities. I hesitate to bring that up because nobody in B.C. wants to hear a reference to that year. That does not mean we’re going to see identical weather,” said Gillham.
“We think the focus might be a bit further east,” centring on the southern Prairies, he said.
The B.C. coast is expected to see near-normal temperatures and precipitation, with the exception of a wetter-than-normal forecast near the Yukon boundary. Into the central and southern interior, conditions are forecasted to be warmer and drier than normal, Gillham said.
Heading north, the forecast is calling for above-normal temperatures and near-normal precipitation across much of the territories where Gillham said he’d be watching closely for wildfire activity. The exceptions are western Yukon, where the forecast is calling for near-normal temperatures and above-normal precipitation, and northern Baffin Island, which could see near-normal temperatures.
It’s shaping up to be a more typical, but still busy hurricane season, continuing the trend of above-average activity since 2016, Gillham said.
That said, the pattern of the jet stream, the high-altitude band of wind that can steer hurricanes, appears to be more conducive to a storm track into either the northeastern United States or Atlantic Canada, he said. Parts of Ontario and Quebec could end up feeling the remnants of those storms, he said.
“So, you could have fewer storms, but all it takes is one storm to have a high impact,” said Gillham.
Climate change has helped ramp up ocean temperatures in the Atlantic, which scientists say may be intensifying hurricanes. Last year brought 18 named storms, including the earliest Category 5 hurricane on record, Beryl.
This year, Environment and Climate Change Canada says experts are predicting about 13 to 19 named storms, six to 10 hurricanes and three to five major hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean basin. Hurricane season runs from June through the end of November.
The Weather Network’s summer forecast says above-normal temperatures and precipitation are expected across most of the Maritimes and western Newfoundland, with some occasional cold fronts. Near-normal precipitation is projected for Newfoundland and Labrador and eastern Nova Scotia, the forecast says.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published May 28, 2025.
Jordan Omstead, The Canadian Press
30-29




